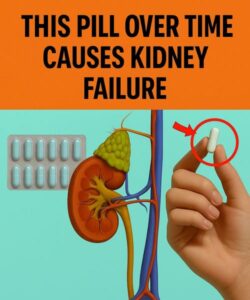
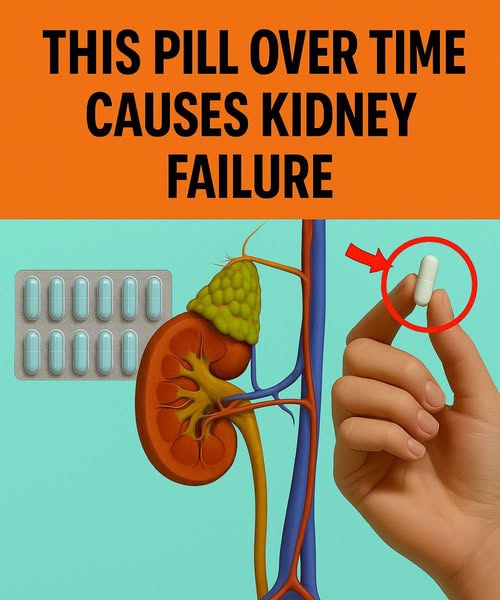
Kidney health is often ignored until the first serious symptoms show. More than 800 million people worldwide deal with chronic kidney disease, often silent until a urine test reveals the presence of albumin, a protein that implies kidney damage. Among the factors that most influence this deterioration is the excessive or improper use of certain medications.
Below, we list some of the most popular medications that, if not used properly, can give and take your kidney function.
1. Omeprazole and other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Omeprazole is considered to treat reflux, heartburn, and ulcers. However, prolonged use without medical supervision can lead to acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease. It is crucial that use be evaluated by a specialist and that you avoid self-medicating.
Alternative: H2 antagonists, such as famotidine or ranitidine, are generally safer for those without pre-existing kidney damage.
2. Ibuprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
This popular pain reliever can ease bl00d flow to the kidneys and cause acute kidney injury, especially in older adults or people with pre-existing kidney disease. The risk increases with prolonged use or high doses.
Recommendation: do not exceed 10 consecutive days of consumption without medical supervision.
3. Pain relievers such as aspirin, naproxen, and diclofenac
Excessive consumption of NSAIDs boosts fluid retention, increases bl00d pressure, and can spark chronic kidney disease. Symptoms include bloating, fatigue, nausea, and decreased urination.
4. Aminoglycoside antibiotics
Drugs such as gentamicin or amikacin, although effective against serious infections, can lead to nephrotoxicity, affecting the nephrons that refine blood and produce urine. Their use requires strict medical supervision.
5. Lithium for bipolar disorder
Long-term lithium treatment can cause kidney failure and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Therefore, users should undergo regular monitoring with nephrologists and psychiatrists.
6. Diuretics
Although they help treat hypertension and fluid retention, diuretics increase the workload of the kidneys, which can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and kidney failure over time.
7. Bl00d pressure medications
Some renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors can affect kidney function over time. Despite these findings, they should not be discontinued without medical advice, as they are essential for controlling hypertension.
Tips and recommendations to protect your kidneys
Manage your blood pressure with regular checkups.
Keep a healthy weight by reducing excess weight.
Control your bl00d sugar levels if you are diabetic.
Have regular urine tests to detect proteinuria.
Avoid self-medication, even with over-the-counter medications.
Get rid of harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Controls cardiovascular factors such as cholesterol and triglycerides.